The Judicial Branch
Structure of the Federal Court System
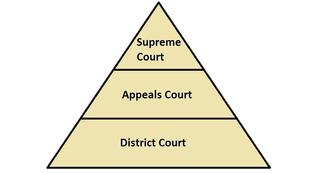
Three tiered system: S.A.D.
S: Supreme Court
A: Appeals Court
D: District Court
S: Supreme Court
A: Appeals Court
D: District Court
District Courts
- 94 in the U.S.
- District Courts are trial courts - they have a judge, a defendant, prosecuting attorney, and a jury that decides innocence or guilt
- General Jurisdiction - they hear cases involving many different issues
Appeals Courts
- 13 in the U.S.
- If you believe that you have been treated unfairly, or that your constitutional rights have been violated in the district court, you can appeal, bringing you to the Appeals Court.
- NOT trial courts
- Panel of judges decides if the other court made an error
- Do NOT determine innocence or guilt
- You can appeal one more time and go to the Supreme Court
Supreme Court
- Highest court of the land
- Consists of 9 justices - 8 associate justices and 1 chief justice
- They decide which cases to hear (less than 0.5% of 1% of all cases
- Rule of 4 - 4 of the 9 justices must agree to hear the case
Types of Law
1. Common Law

"Duh!" Laws - Based on common sense or longstanding tradition
EX: Don't drive backward down the road, there is no law that says you can't but you will still get a ticket.
EX: Don't drive backward down the road, there is no law that says you can't but you will still get a ticket.
2. Statutory Law

Law passed by a law making body
Think of a law. Speeding? Murder? That's a Statutory Law.
Think of a law. Speeding? Murder? That's a Statutory Law.
3. Constitutional law

Law stated in the Constitution
EX: Protection from cruel and unusual punishment
EX: Protection from cruel and unusual punishment
4. Administrative Law

Law made by a government agency
EX: The FCC says that it is against the law to show obscene or profane programs on television during certain times of the day.
EX: The FCC says that it is against the law to show obscene or profane programs on television during certain times of the day.
Types of Cases in Federal Court
Crimes committed in a ship at sea

EX:
If someone was murdered on a cruise ship.
Though it is old, piracy is a crime on the sea.
If someone was murdered on a cruise ship.
Though it is old, piracy is a crime on the sea.
State vs. State lawsuits
EX: If Wisconsin decided to sue Illinois for more land.
Breaking a law created by Congress

EX: Murder
Violating the Constitution

EX: Not allowing an African American to vote.
Violating a U.S. Treaty
EX: The Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement - it is against the law to dump pollution into any of the Great Lakes that will affect the wildlife there.
Lawsuits from citizens of different states
Most Common
EX: If someone from Kentucky stole from a person in Tennessee
EX: If someone from Kentucky stole from a person in Tennessee
Famous Cases
Santa Fe Independent School District v. Jane Doe (2000)

Before home football games, a student who had been elected by his peers led a prayer over the announcements. The school was sued by some of the students and their parents because of the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment ("Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof.")
Ruling: The school was being unconstitutional. The students may have led the prayer, the school still sponsored it. It was unconstitutional because even students that had different religious beliefs had to sit and listen, there was no way for them to escape the prayer.
Ruling: The school was being unconstitutional. The students may have led the prayer, the school still sponsored it. It was unconstitutional because even students that had different religious beliefs had to sit and listen, there was no way for them to escape the prayer.
Ingraham v. Wright (1997)

James Ingraham was an eighth-grader at Drew Junior High School in Miami. He was accused of being rowdy so his teacher sent him to the principal's office. As punishment, the principal was going to swat him five times with a paddle but when James wouldn't allow it, he ended up suffering twenty swats instead. James missed school and had to seek medical attention for his bruises. He and his mother sued the principal and other school officials saying that James' punishment was "cruel and unusual".
Ruling: James and his mother did not win their case, but the court did advise schools to be careful about using corporal punishment. They said that the Eighth Amendment was not for mischievous kids.
Ruling: James and his mother did not win their case, but the court did advise schools to be careful about using corporal punishment. They said that the Eighth Amendment was not for mischievous kids.
DeShaney v. Winnebago Countny Social Services (1989)

Joshua DeShaney was four years old. He was taken into custody by Social Services when they found out his father was physically abusing him but he was returned to his father in three days. The abuse continued and escalated to a point where Joshua was hospitalized and suffered severe brain damage and was permanently paralyzed. Joshua's father was sent to prison for the abuse and Joshua's mother sued Social Services because they had given Joshua back to his father. She said they had violated Joshua's Fourteenth Amendment forbidding the state from depriving"any person of life, liberty,or property, without due process of the law.
Ruling: The court decided that the Constitution does not protect children from their parents so Joshua and his mother got nothing for his abuse.
Ruling: The court decided that the Constitution does not protect children from their parents so Joshua and his mother got nothing for his abuse.

